Stinging nettle
| Stinging nettle |
|---|

|
| Scientific Classification |
|
| Binomial Name |
|
Urtica dioica |
The stinging nettle is a species of plant known by the scientific name Urtica dioica. It is best known for the skin irritations it causes upon contact, but it is also used in many home remedies.
Anatomy
Nettles grow 1-2 meters tall [1].
roots
The roots are distinctively yellow [2].
stem
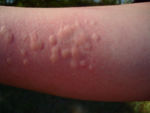
The stem is used to transport materials up and down the plant via the xylem and the phloem. The stem on the stinging nettle is covered in hollow hairs that contain Histamine, a skin irritant [3], Acetylcholine which induces a burning sensation in the skin[4], and Serotonin which encourages the other to chemicals to react more violently[5].
leaves
The leaves are covered with silky, brittle, hollow hair [6]. The leaves are 3-15 cm long[7].
Hairs
The hairs contain the three different chemicals [8]: Histamine [9], Acetylcholine[10] and Serotonin. The chemicals are released when the hairs are broken by an outside source[11]. A person may avoid breaking the hairs by stroking the leaf down the middle in the direction that the hairs flow [12].
Reproduction
Stinging nettles reproduce sexually and asexually through self-pollination.
Ecology
Location
Stinging nettles may be found in North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Northern Africa [13]. In America it may be found anywhere except for Hawaii [14]. In the UK, stinging nettles have an affinity for abandoned human buildings, especially fenced farmlands which were abandoned during the great potato famine[15]. This might only be due to the higher levels of phosphate in the ground, from improper disposal of human waste, or because animal waste was used as a fertilizer around the structures[16].
Uses
Stinging nettles are edible if prepared properly and may be used to cure minor afflictions.
medical
When the stinging nettle is eaten along with lots of liquids, the nettle increases the flow of urine, helping to flush out infections from the urinary tract, along with helping to stop the formation of kidney stones [17]. A clinical study supports this effect concerning the root as well[18]. The stem and leaves may be brewed in a tea that helps relieve arthritis pain [19]. In a case study it was shown that 57% of those tested found that stinging nettles relieved hay fever better than the placebo[20].
People should not use this herb if they have fluid retention due to heart failure or kidney problems, since these serious problems require a medical doctor [21].
Chemical Components
The leaves and other above ground foliage contain salts, potassium and calcium[22]. There are also some volatile oils present [23]. In the above ground foliage silica acid composes 1-4% of the plant along with 1.8% of various flavonoids [24]. In the roots different vitamins are present such as C, K, and B [25].
first aid
If someone comes in contact with a stinging nettle, they should wash the contaminated area immediately to try to remove most of the chemicals. If this can't be done immediately, gather the brown spore pods from the underside of leaves of the sword fern and grind them into a paste to apply to the rash. If sword fern cannot be found apply horsetail juice from the stem, or crushed dock leaves [26].
Gallery
References
- Wikipedia version by Wikipedia. Wikipedia.
- Nettles (Urtica species, Laportea canadensis by anynomous.
- Stinging Nettle Herb Library by Joe and Terry Graedon. People's Pharmacy.