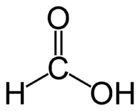
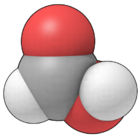
Formic acid
| Formic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Methanoic acid |
| Other names |
Hydrogen carboxylic acid |
| Molecular formula | CH2O2 HCOOH |
| SMILES | O=CO |
| Molar mass | Molar mass::46.0254 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| CAS number | CAS number::64-18-6 |
| Properties | |
| Density and phase | [[Density::1.22 g/cm3]], liquid |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| Melting point | Melting point::8.4°C |
| Boiling point | Boiling point::100.8°C |
| Acidity | 3.744 |
| Viscosity | 1.57cP at 26°C |
| Structure | |
| Coordination geometry |
Planar |
| Dipole moment | 1.41 D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS Data |
| Main hazards | moderate fire hazard corrosive, irritant, sensitizer |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 69°C (156°F) |
| R/S statement | R: skin burns or eye damage. trouble breathing S: Wear skin protection (gloves) and goggles. |
| RTECS number | LQ4900000 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related carboxylic acids | acetic acid, propionic acid |
| Related compounds | formaldehyde methanol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Disclaimer and references | |
Formic Acid occurs naturally and was first discovered in 1671 in the bodies of ants. This acid is also found in the natural state of stinging nettles and bees, causing whoever to come in contact with them to have a burning and irritated feeling. [1] [2]
Properties
Formic acid shares most of the chemical properties of other carboxylic acids. Heat can cause formic acid to decompose to carbon monoxide and water. Formic acid shares some of the reducing properties of aldehydes. Formic acids and alkenes react to form formate esters. In the presence of certain acids, including sulfuric and hydrofluoric acids, a variant of the Koch reaction takes place instead, and formic acid adds to the alkene to produce a bigger carboxylic acid.[3]
Occurrences
English naturalist John Ray discovered formic acid. he took a number of distilled dead ants and extracted the acid out of them. In nature is found in ants. The ants use it as a self defense or and attack. They are also found in stinging nettles bee stings and some insects. All of which are used as a defense mechanism.[4]
Uses
The main use for Formic Acid to day would be in preserving food for livestock. It helps slow down the decaying process and allows for the food to contain a more nutritive value for a longer period of time. Other smaller uses are: "It is importance in the textile industry and for the tanning of leather. It is used to process organic latex into rubber. and is used in laboratories as a solvent modifier for HPLC separations of proteins and peptides". [5]
Other
In storing formic acid, keep in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry, ventilated area away from sources of heat or ignition. Also protect against any physical damage. Store separately from reactive or combustible materials, and out of direct sunlight. If it is highly corrosive it should be handled in 316 stainless steel, glass, ceramic, or similar corrosion resistant materials.
References
- Formic acid Many Authors. wikipedia.
- link title Author. Publisher.
- Methanoic acid Many Authors. Publisher.
- [6]Mathieu Laffitte.google.
| ||||||||||||||


